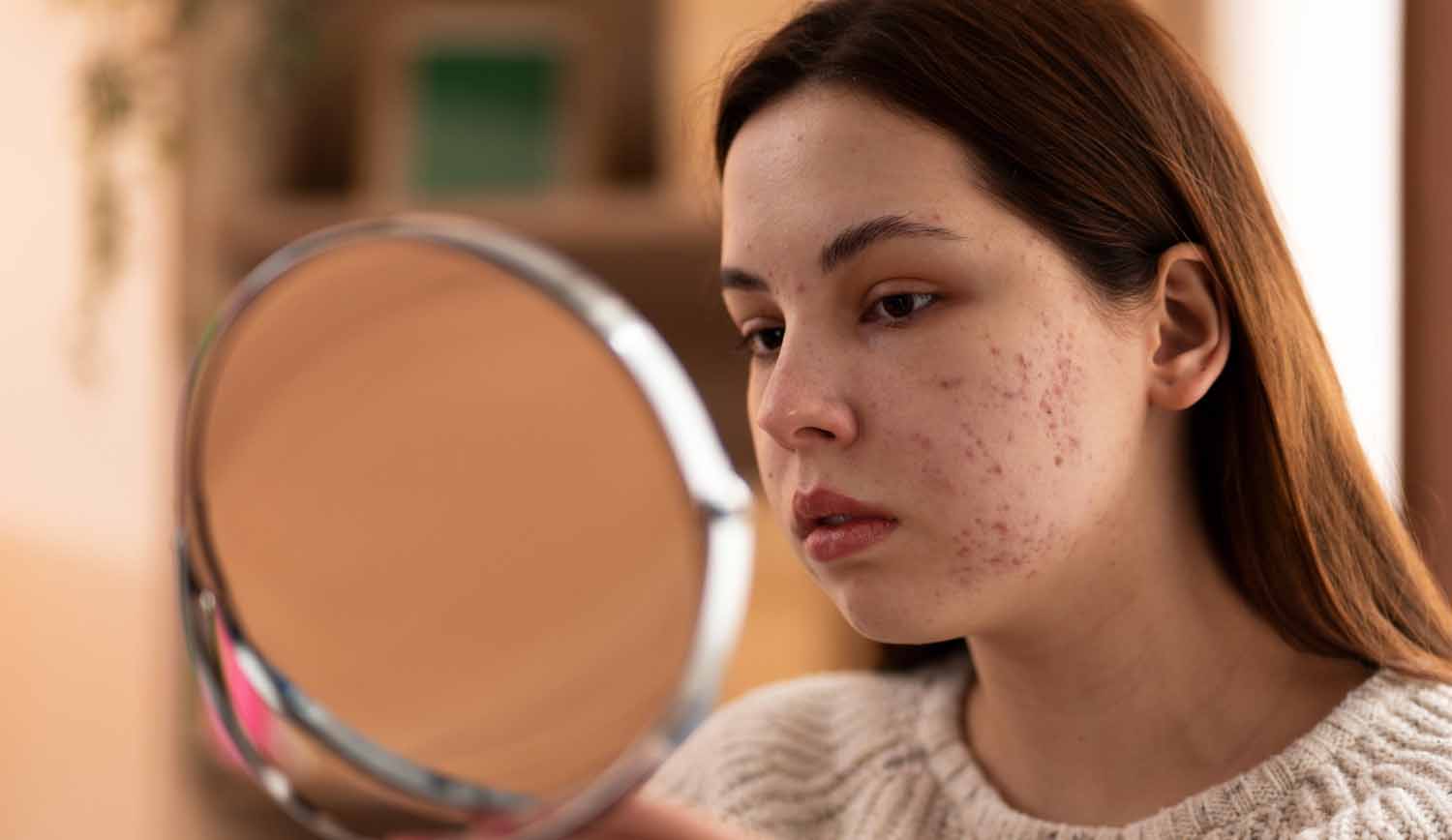
Dealing with acne can be tough, no matter your age. Whether you’re a teenager with breakouts or an adult facing stress-related acne, finding a routine that works is key to clear skin. Welcome to “Clear Skin Secrets,” where we’ll share the best routine for managing acne.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through an easy and effective skincare routine. From washing your face to choosing the right moisturizer, each step is designed to help you fight acne and keep your skin healthy. Say goodbye to pimples and hello to clear, glowing skin. Let’s get started on the path to your best skin ever!
Causes of Acne:
1. Excess Oil Production:
The skin’s sebaceous glands produce sebum, an oily substance intended to lubricate the skin and hair. When these glands become overactive, they produce excess sebum, which can combine with dead skin cells and clog hair follicles. Hormonal changes, particularly an increase in androgens, can stimulate these glands to produce more oil. This excess oil is a primary factor in the development of acne.
2. Clogged hair follicles:
Hair follicles, also known as pores, can become clogged when dead skin cells are not shed properly. Instead of rising to the surface and sloughing off, the cells remain within the follicle, mixing with excess sebum to form a plug. This plug can create an environment where bacteria thrive, leading to the formation of comedones (whiteheads and blackheads).
3. Bacteria:
The skin naturally hosts various bacteria, including Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes). While typically harmless, when a pore is clogged with oil and dead skin cells, it creates an anaerobic (low-oxygen) environment where P. acnes can multiply rapidly. The presence of this bacteria can cause the body’s immune system to respond, leading to inflammation and the characteristic redness and swelling of acne.
4. Hormonal Changes:
Hormones, especially androgens, can increase the size and activity of the sebaceous glands, resulting in more sebum production. During puberty, hormonal fluctuations are common, making acne prevalent among teenagers. Women may experience acne flare-ups due to hormonal changes during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) also involve hormonal imbalances that can exacerbate acne.
5. Inflammation:
Inflammation is a significant component of acne. When the body detects the presence of bacteria in a clogged pore, it triggers an inflammatory response. This response can cause the pores to swell and become red, tender, and painful. Chronic inflammation can also lead to more severe forms of acne, such as cysts and nodules, which are deep-seated, painful lesions that can cause scarring.
6. Diet:
Emerging research suggests a link between diet and acne. High-glycemic-index foods, which cause rapid spikes in blood sugar, can lead to increased insulin levels. Insulin, in turn, can stimulate sebum production and exacerbate acne. Dairy products, especially those containing hormones, can also contribute to acne in some individuals. Diets high in processed foods and sugars may promote inflammation and influence acne development.
7. Stress:
Stress can exacerbate acne through the production of cortisol and other stress hormones. These hormones can increase oil production in the skin and contribute to inflammation. Additionally, stress can impact other factors such as sleep and diet, which in turn can affect skin health. Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and adequate sleep can help mitigate its impact on acne.
8. Medications:
Certain medications can induce or worsen acne. Corticosteroids, often used for their anti-inflammatory properties, can increase oil production in the skin. Lithium, used for bipolar disorder, and certain anticonvulsants used to treat epilepsy, can also lead to acne development. It’s important for individuals experiencing medication-induced acne to consult with their healthcare provider for potential alternatives or solutions.
9. Genetics:
Genetics plays a significant role in determining one’s susceptibility to acne. If your parents had acne, you are more likely to experience it as well. Genetic factors influence skin characteristics, such as the size and activity of sebaceous glands, the body’s inflammatory response, and how skin cells are shed and renewed. Understanding your genetic predisposition can help in tailoring appropriate treatments and preventive measures.
10. Cosmetics and Skincare Products:
Some cosmetic and skin care products contain ingredients that can clog pores, leading to acne. These are known as comedogenic products. Individuals prone to acne need to use non-comedogenic or oil-free products. Ingredients to avoid include heavy oils and certain silicones. Proper skin hygiene, including thorough cleansing to remove makeup and debris, is crucial in preventing cosmetic-induced acne.
11. Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors such as pollution, high humidity, and exposure to certain chemicals can exacerbate acne. Pollutants can accumulate on the skin and mix with sebum, leading to clogged pores and inflammation. High humidity can increase sweat and oil production, contributing to acne. Additionally, occupational exposure to oils, greases, and other industrial substances can provoke acne. Protecting the skin with appropriate products and maintaining a clean environment can help mitigate these factors.
The Best Routine for Managing Acne at Home

Morning Routine
1. Cleanser:
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face. Look for products with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to help control oil and prevent breakouts.
2. Toner:
Apply a toner containing ingredients like witch hazel or salicylic acid to help remove excess oil and tighten pores.
3. Serum:
Use a serum with niacinamide or hyaluronic acid to help with hydration and reduce inflammation.
4. Moisturizer:
Even if you have oily skin, use a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated without clogging pores.
5. Sunscreen:
Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30. Sunscreen protects your skin from UV damage and helps prevent acne scars from darkening.
Evening Routine
1. Cleanser:
Wash your face with the same gentle cleanser you used in the morning to remove makeup, dirt, and oil accumulated throughout the day.
2. Exfoliant (2–3 times a week):
Use a chemical exfoliant with AHAs (like glycolic acid) or BHAs (like salicylic acid) to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores. Avoid physical scrubs that can irritate the skin.
3. Toner:
Apply your toner again to balance your skin’s pH and prepare it for the next steps.
4. Treatment:
Use a spot treatment containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid on active breakouts.
5. Serum:
Apply a serum with ingredients like retinol, which helps to increase cell turnover and prevent clogged pores. Use retinol every other night if your skin is sensitive.
6. Moisturizer:
Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated. Look for ingredients like ceramides or peptides to support your skin barrier.
Weekly Additions
1. Clay Mask (1-2 times a week):
Use a clay mask to absorb excess oil and draw out impurities from your pores.
2. Hydrating Mask (1-2 times a week):
Use a hydrating mask to keep your skin balanced and moisturized, especially if you are using drying acne treatments.
Best Tips for Acne
Here are some of the best tips for managing and preventing acne:
1. Cleanse Gently:
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser twice daily (morning and evening) to remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities without stripping the skin of its natural oils.
2. Moisturize regularly:
Even if you have oily skin, use an oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated. Proper hydration helps maintain a healthy skin barrier.
3. Use non-comedogenic products:
Choose skincare and makeup products labeled as non-comedogenic, which means they won’t clog pores and contribute to acne.
4. Spot treat with Benzoyl Peroxide or Salicylic Acid:
Apply a targeted spot treatment containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid directly onto pimples to reduce inflammation and speed up healing.
5. Don’t over-exfoliate:
Exfoliating too often or using harsh scrubs can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Limit exfoliation to 2-3 times per week and choose gentle chemical exfoliants like AHAs or BHAs.
6. Protect your skin from the sun.
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Sunscreen protects against UV damage and prevents acne scars from darkening.
7. Avoid touching your face.
Touching your face can transfer bacteria and oils from your hands, worsening acne. Avoid picking or squeezing pimples, as it can lead to scarring and further inflammation.
8. Manage stress:
Stress can trigger hormonal changes that contribute to acne. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
9. Watch your diet:
Some studies suggest that dairy products and high-glycemic foods (like sugary snacks and refined carbohydrates) may worsen acne in some individuals. Consider reducing your intake and observing how your skin responds.
10. Keep your hair clean and away from your face.
Oily hair can contribute to acne on the forehead and temples. Wash your hair regularly and keep it away from your face, especially if you use styling products.
11. Change pillowcases and towels regularly.
Dirty pillowcases and towels can harbor bacteria and oil, which can transfer to your skin and worsen acne. Change them at least once a week.
12. Consult a dermatologist:
If over-the-counter treatments aren’t effective, or if you have severe acne, consult a dermatologist. They can prescribe medications or recommend treatments tailored to your skin type and condition.
Conclusion:
Getting clear, acne-free skin takes time, consistency, and the right routine. By following the steps in this blog, you’re on your way to healthier skin.
Use gentle cleansers, and effective treatments, and keep your skin well-hydrated. Avoid harsh products, and remember to eat well and drink plenty of water. Pay attention to how your skin reacts and adjust your routine as needed.
Clear skin doesn’t happen overnight, but with patience and the right care, you can reduce breakouts and improve your skin. Stay dedicated, and you’ll soon see the results of your efforts.
Thanks for reading, and good luck on your journey to clear, glowing skin!


Clear Skin Secrets: The Best Routine for Managing Acne