Protein, a fundamental macronutrient, is a key player in the intricate dance of maintaining optimal health and functionality within the human body. Comprising essential amino acids, the building blocks of life, proteins play a multifaceted role in supporting various bodily functions. From facilitating muscle growth and repair to contributing to the structure of cells and tissues, protein serves as an indispensable component in the intricate tapestry of human nutrition. This versatile macronutrient extends its influence beyond mere physical structure, also participating in the regulation of enzymes, hormones, and immune responses. Understanding the significance of protein provides a foundational perspective on its vital role in promoting overall well-being and sustaining the intricate balance of the human body. Here in this article Best High Protein Foods for Optimal Nutrition.
Why we Need Protein
The body’s building blocks are proteins. They are composed of vitamins, hormones, enzymes, skin, blood, muscle, cartilage. In addition to being necessary for normal bodily functions including blood coagulation, fluid balance, and the immune system, they also repair and construct cells and tissue, including muscle. Amino acids are found in proteins. Certain amino acids are naturally produced by our bodies. We refer to these amino acids as non-essential. However, our bodies require nine amino acids, which we must obtain from the foods we eat. These are known as essential amino acids, and the body needs them to function normally.
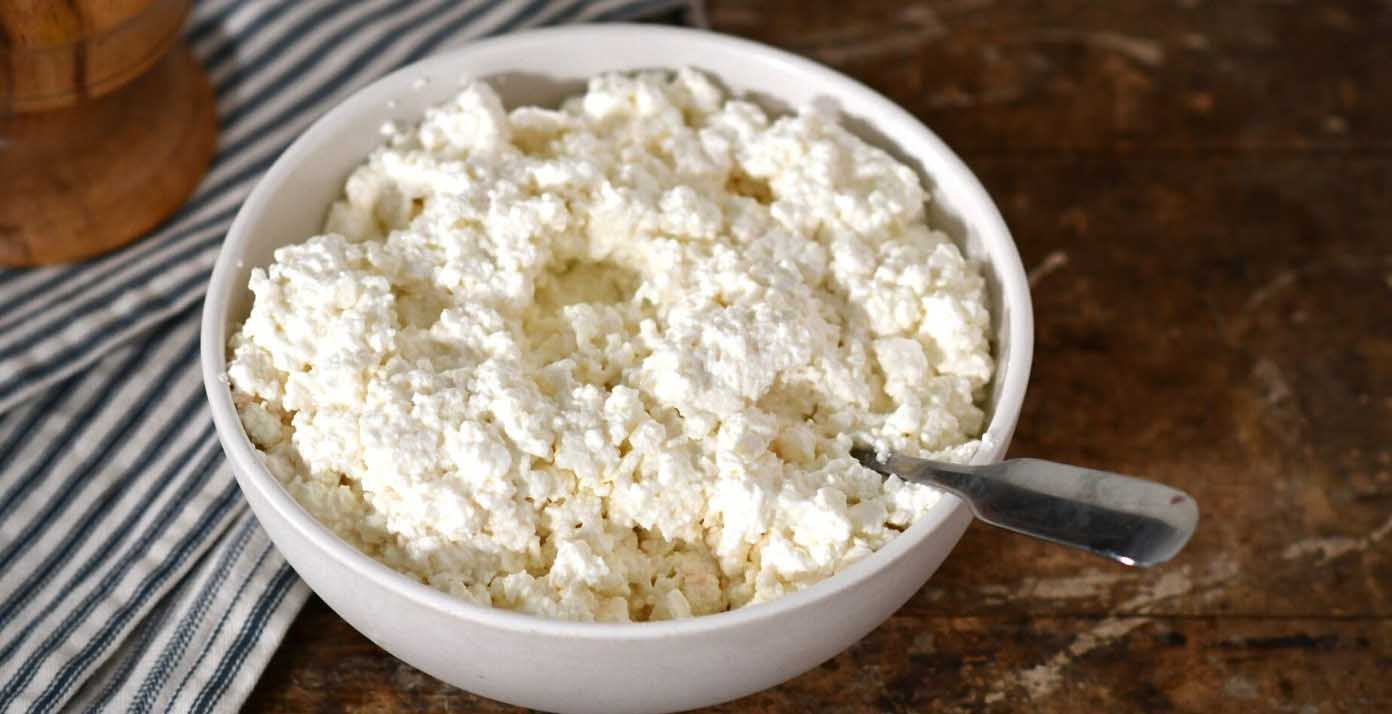
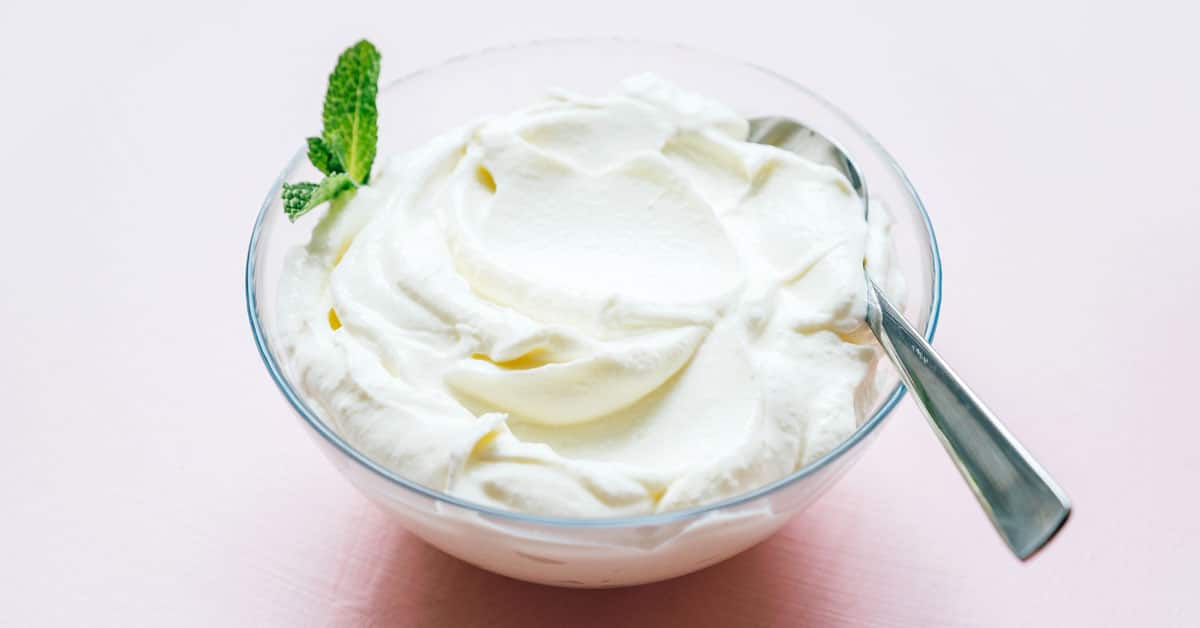
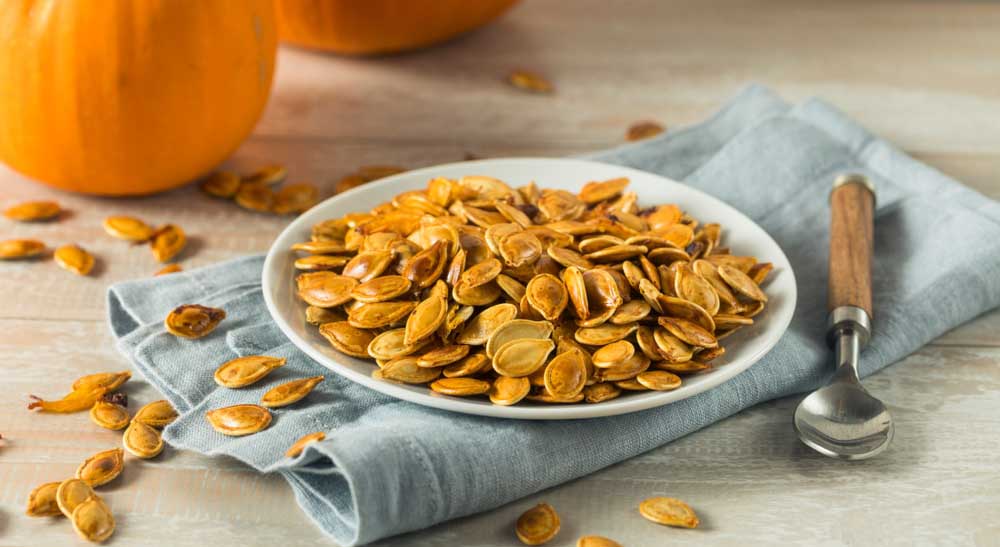
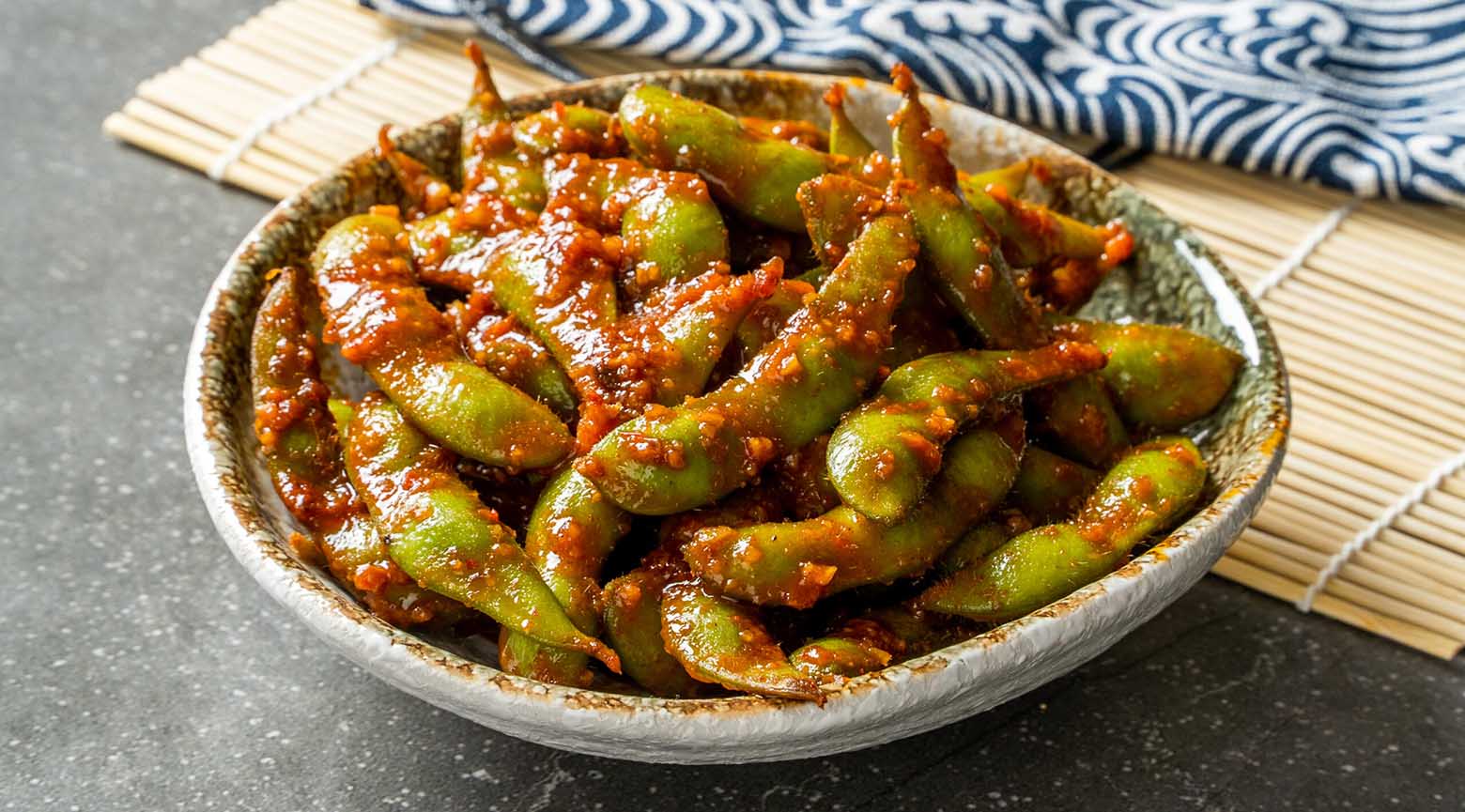
High Protein Foods | Protein Content per 100g (approx.)
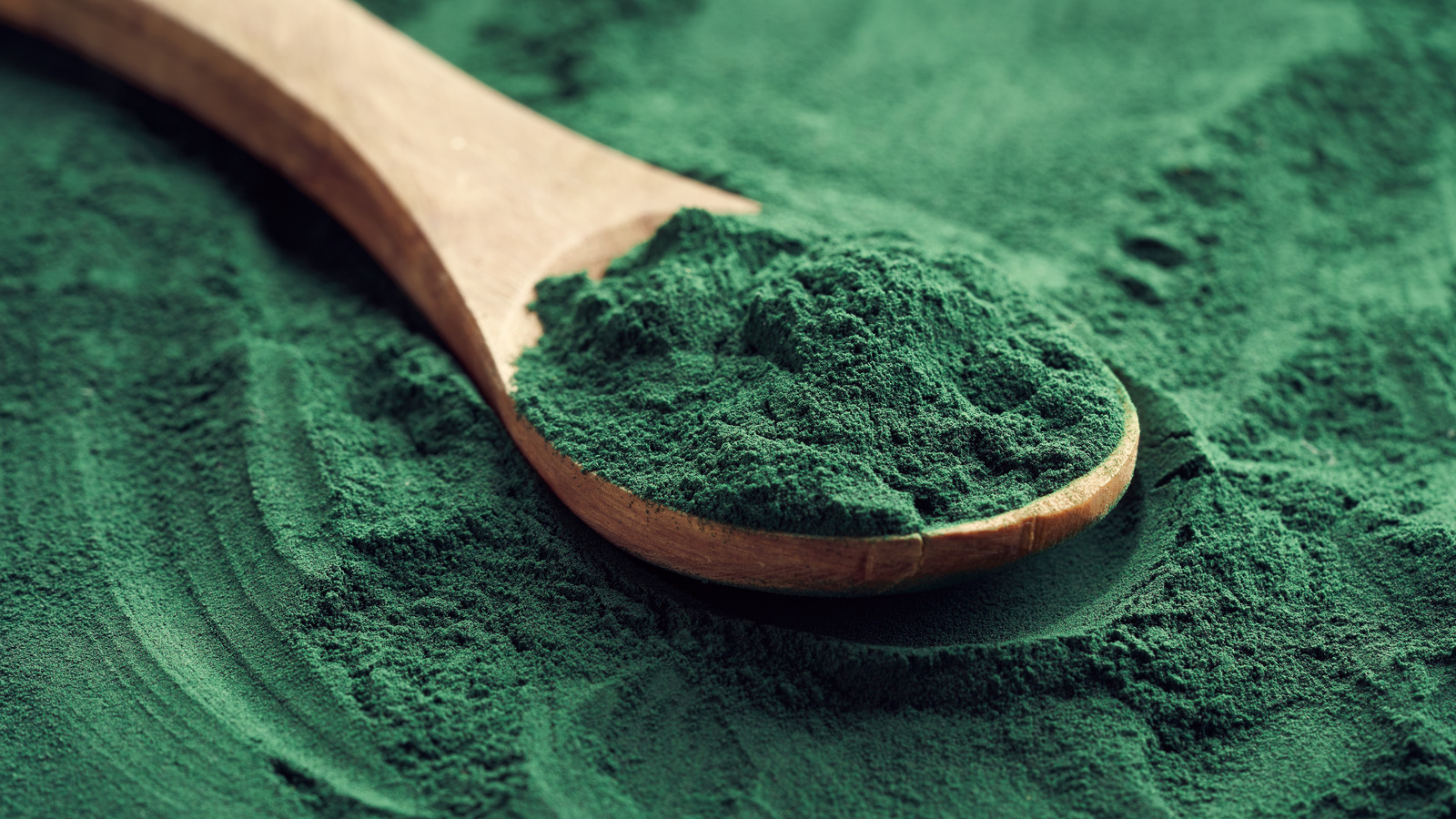
| Spirulina (dried) | 57g |
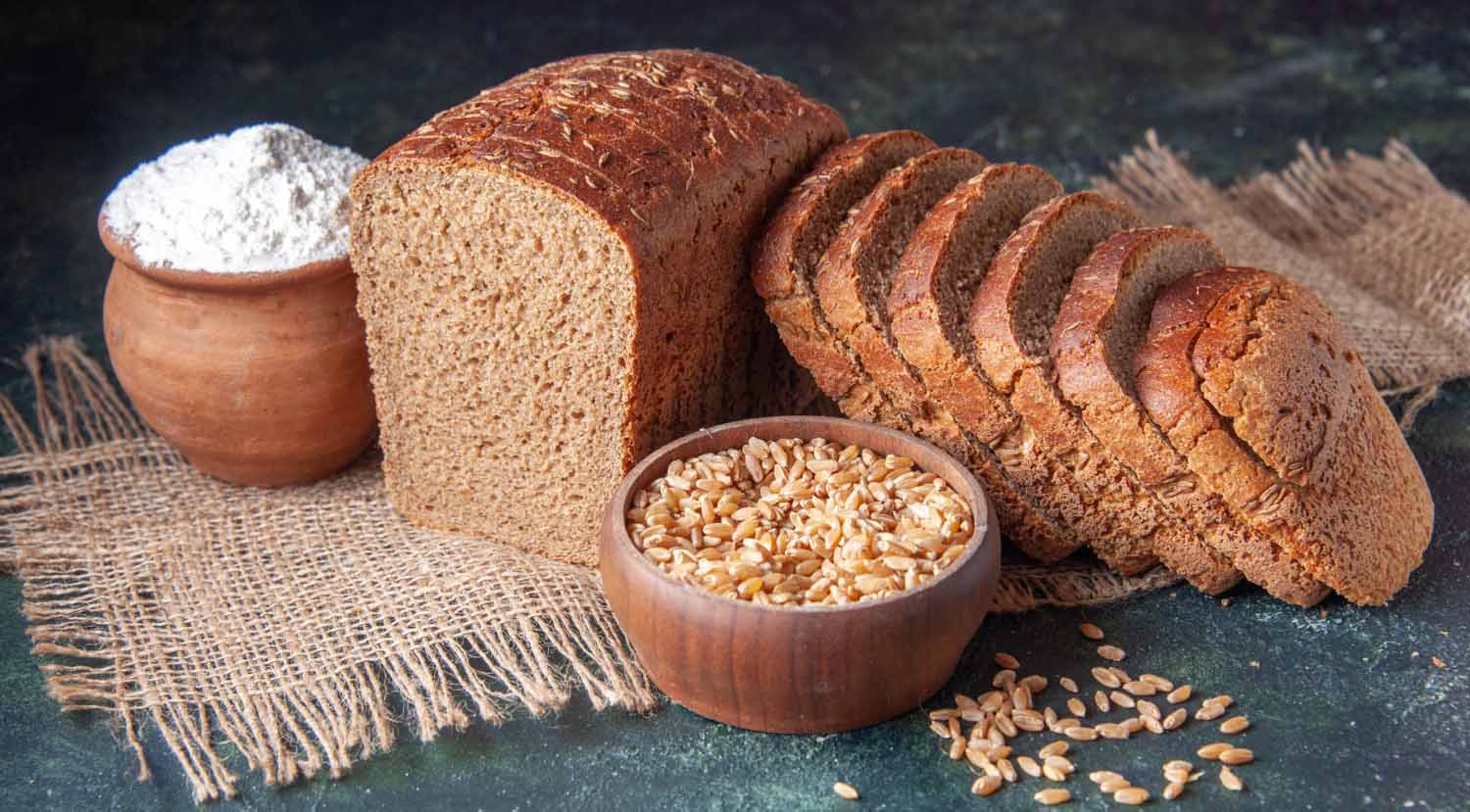
| Seitan (wheat gluten) | 75g |
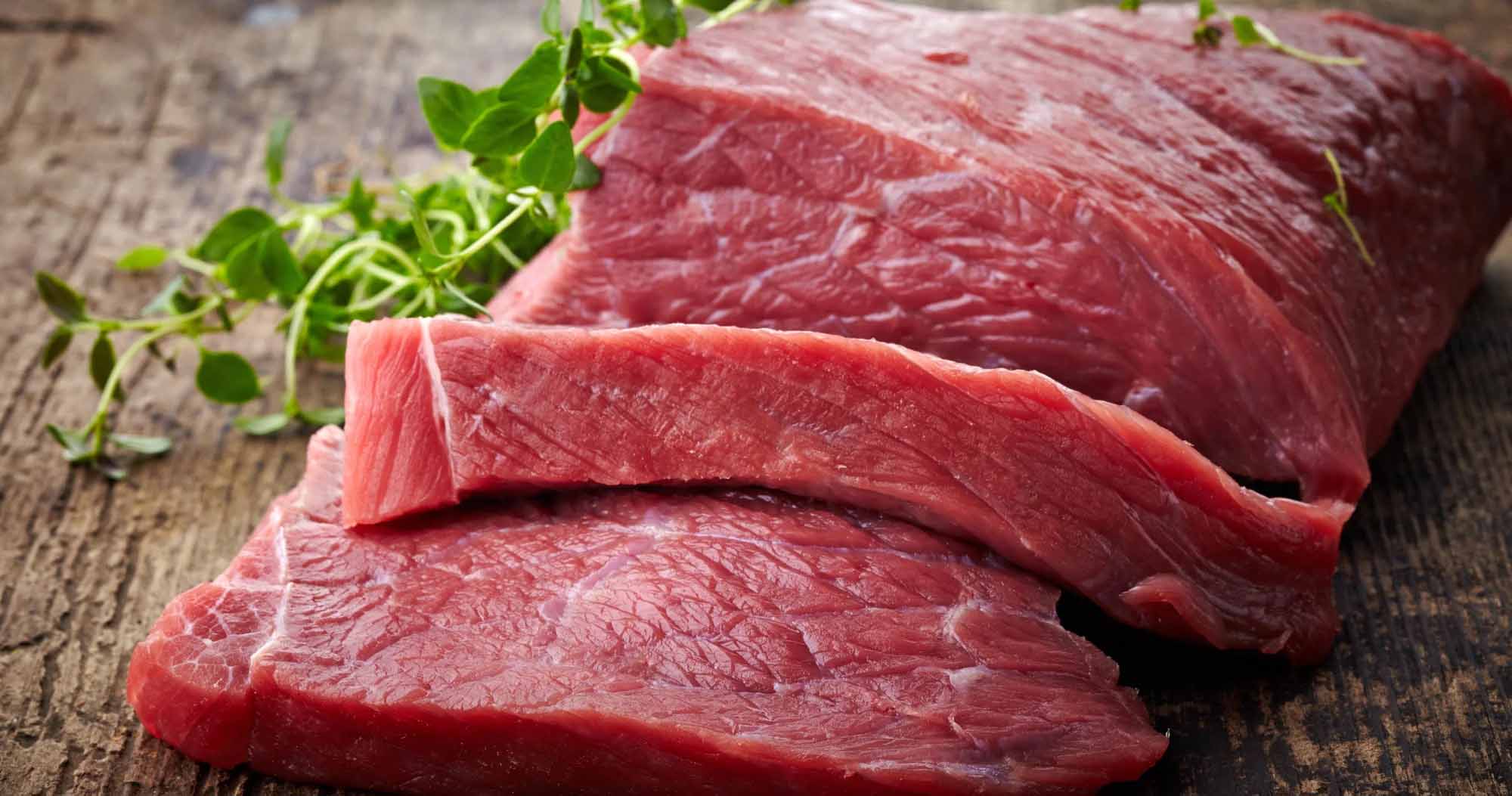
| Ostrich Meat | 29g |
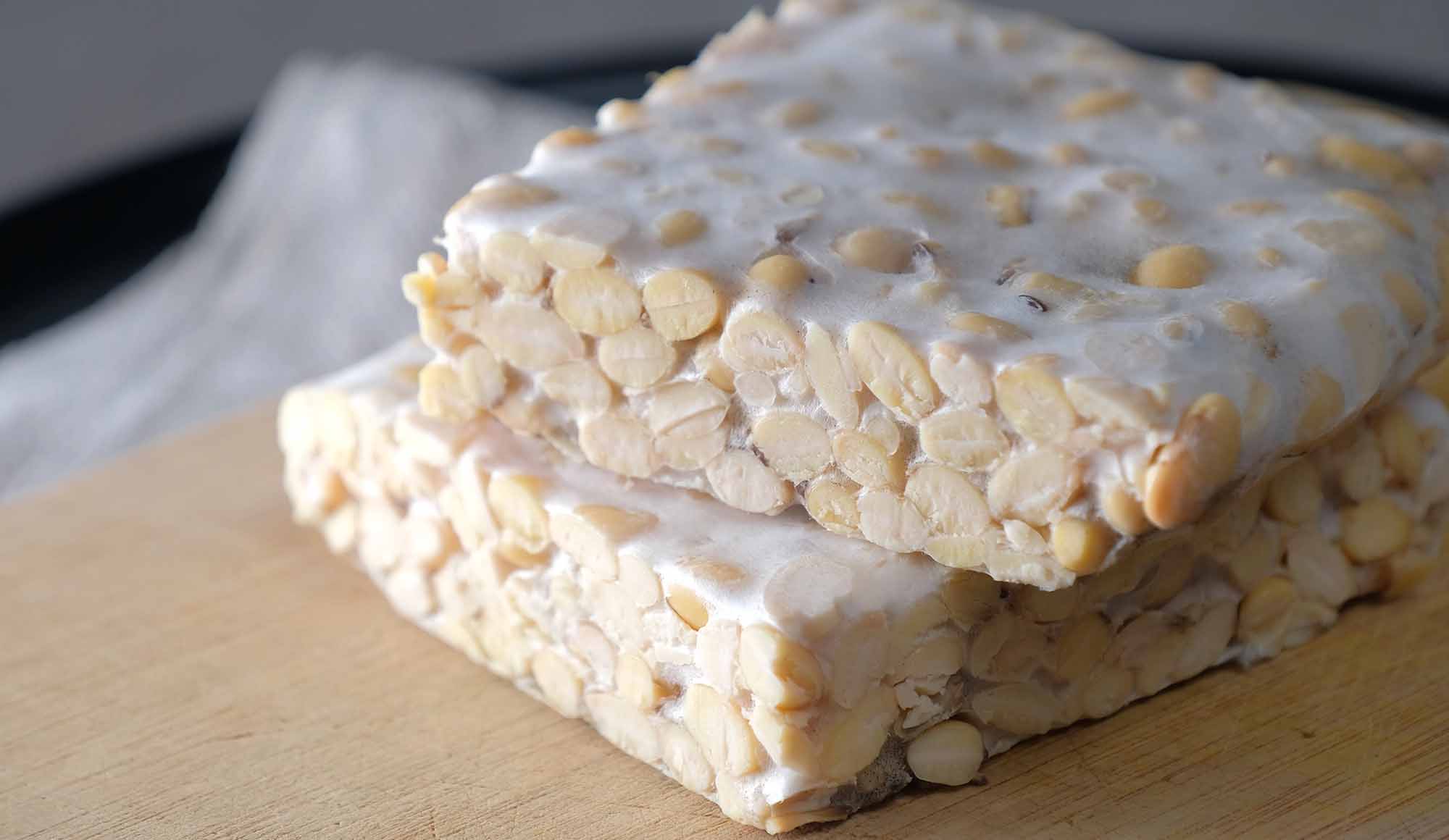
| Tempeh | 19g |
| Cottage Cheese | 11g |
| Greek Yogurt | 10g |
| Pumpkin Seeds | 19g |
| Edamame (cooked) | 11g |
| Bison Meat | 29g |
| Hemp Seeds | 31g |












Maximize Your Protein: Best High Protein Foods for Optimal Nutrition